July 14, 2025
Table of contents
In this guide, you'll learn how to set up Polar with Supabase.
Supabase and Polar are great tools that allow you to easily create a SAAS.
Unfortunately, if you want to use them together, you have to set up a third party server to synchronize the two.
But not anymore...!
What you'll build
In this blog post, you'll learn how to set up polar.sh with Supabase using Supabase's built-in Edge Functions.
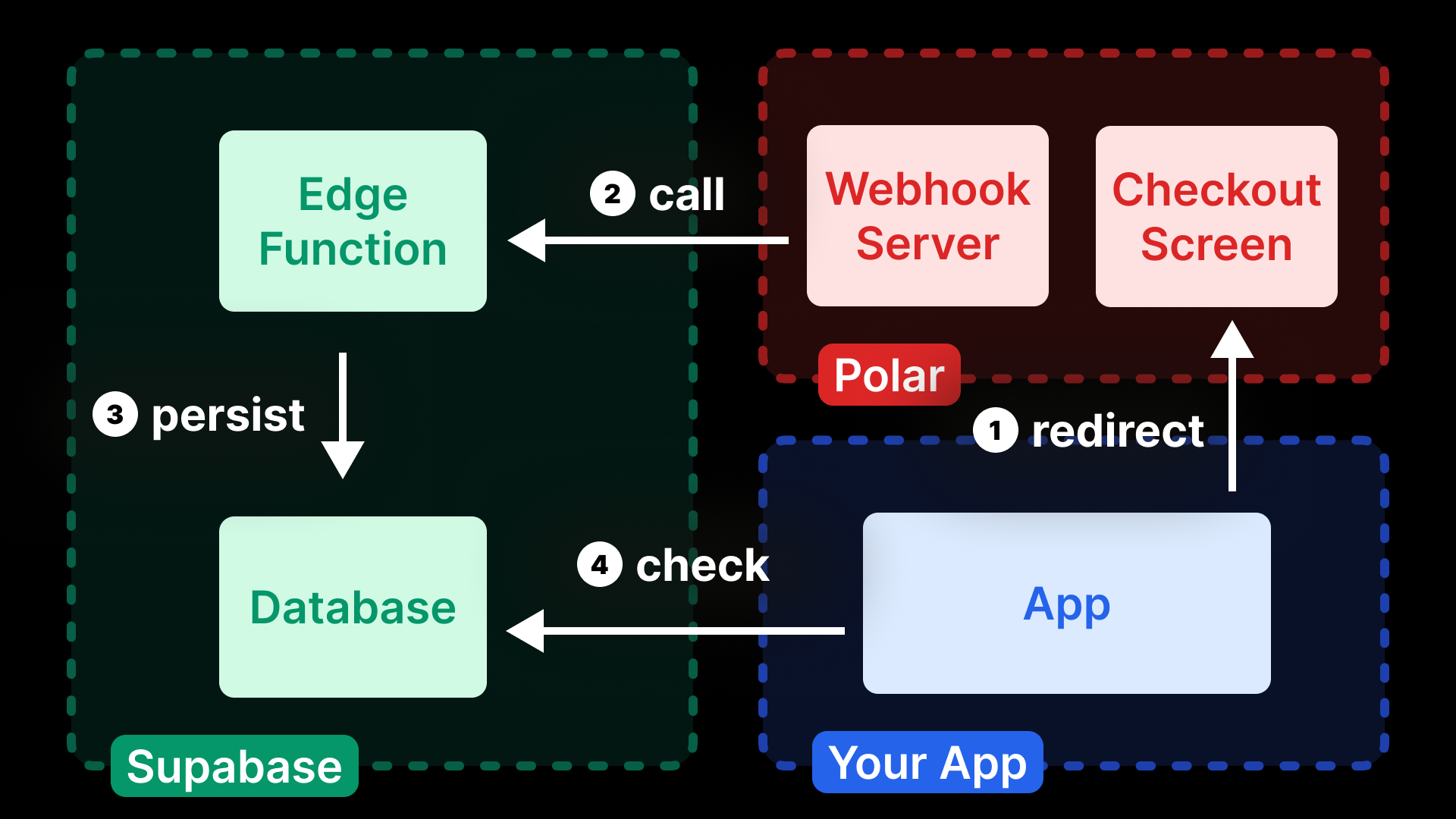
For that, we'll set up a Supabase Edge Function that will listen forPolar's subscription events.
The subscriptions of the users will be saved in a supabase database.
Each user can then read their own subscription state from a dedicated subscriptions database table.
Setup
Step 1: Prefill the Checkout Screen
For that, you can prefill the email field of the checkout page by appending a url parameter to the checkout url.
For example:
https://buy.polar.sh/XXXX?customer_name=Youssef%DBenlemlih&customer_email=email@example.com
You can format a URL by using this example function in TypeScript:
function formatUrl(displayName, email) { return `https://buy.polar.sh/XXXX?customer_name=${encodeURIComponent(displayName)}&customer_email=${encodeURIComponent( email, )}`; }
Step 2: Create a subscriptions Table
This is where the user subscriptions will be saved and read from your app.
Navigate to the Supabase SQL Editor and run the following SQL command to create a new table:
create table public.subscriptions ( user_id uuid not null, user_email character varying not null, created_at timestamp with time zone not null default now(), modified_at timestamp with time zone null default now(), subscription_id text not null, subscription_status text not null, subscription_starts_at timestamp with time zone not null, subscription_ends_at timestamp with time zone null, subscription_price numeric not null, subscription_currency text not null, product_id text not null, product_name text not null, product_recurring_interval text not null, raw_last_event json not null, constraint subscriptions_pkey primary key (user_id, subscription_id), constraint subscriptions_user_id_fkey1 foreign KEY (user_id) references auth.users (id) on update CASCADE on delete CASCADE ) TABLESPACE pg_default;
Notice we're using (user_id, subscription_id) as a primary key.
This is crucial because it assures we don't have double entries for a user subscription.
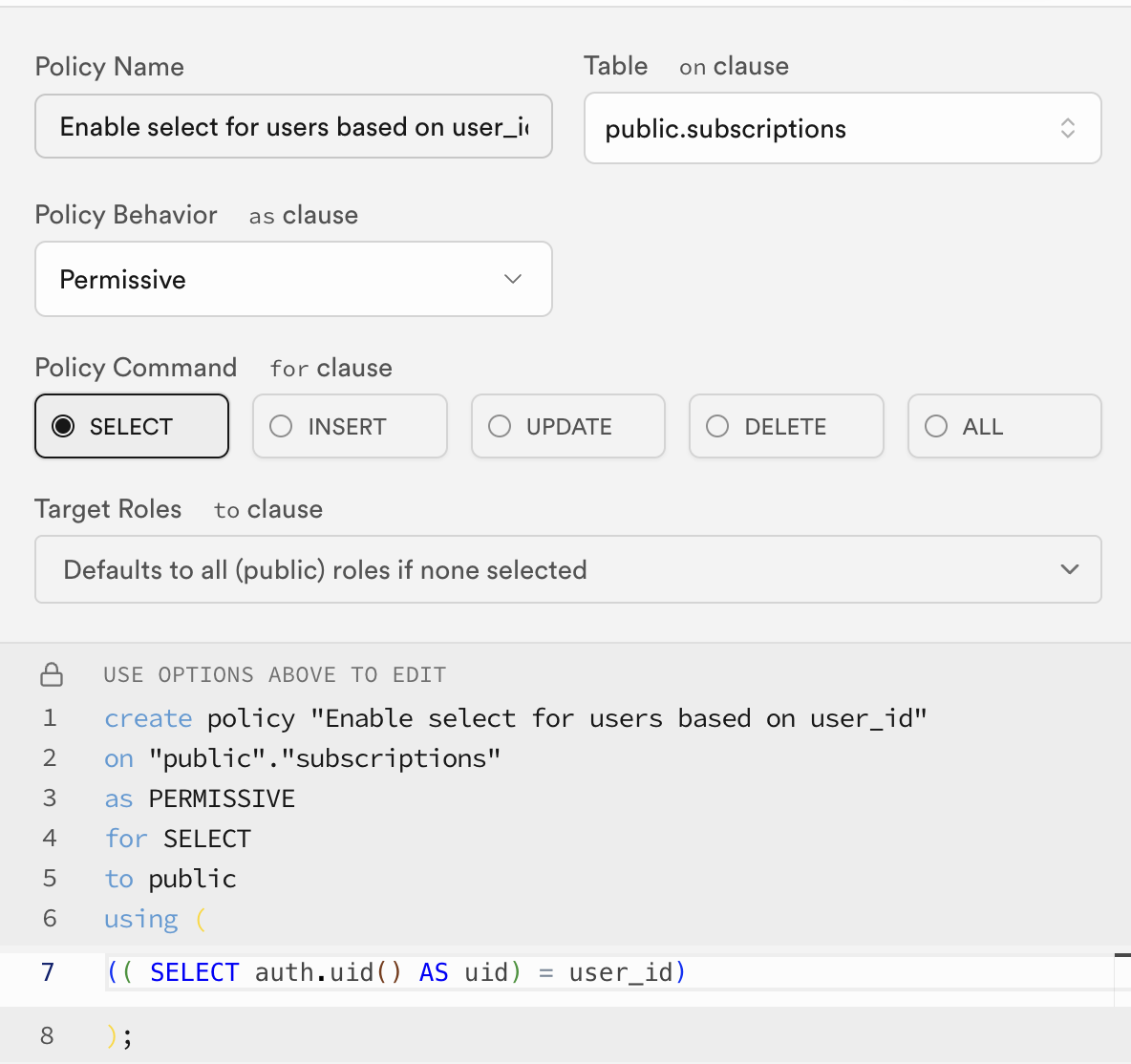
Step 3: Add read policy to Subscriptions
Now let's add a Policy to the Subscriptions table so that each user can read their own subscription.
Navigate to the Policies page and add a new Policy with these values:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name: | Enable select for users based on user_id |
| Action: | PERMISSIVE |
| Command: | SELECT |
| Target roles: | public (leave unchanged) |
| USING expression: | (( SELECT auth.uid() AS uid) = user_id) |
| CHECK expression: | None |
It should look like this:
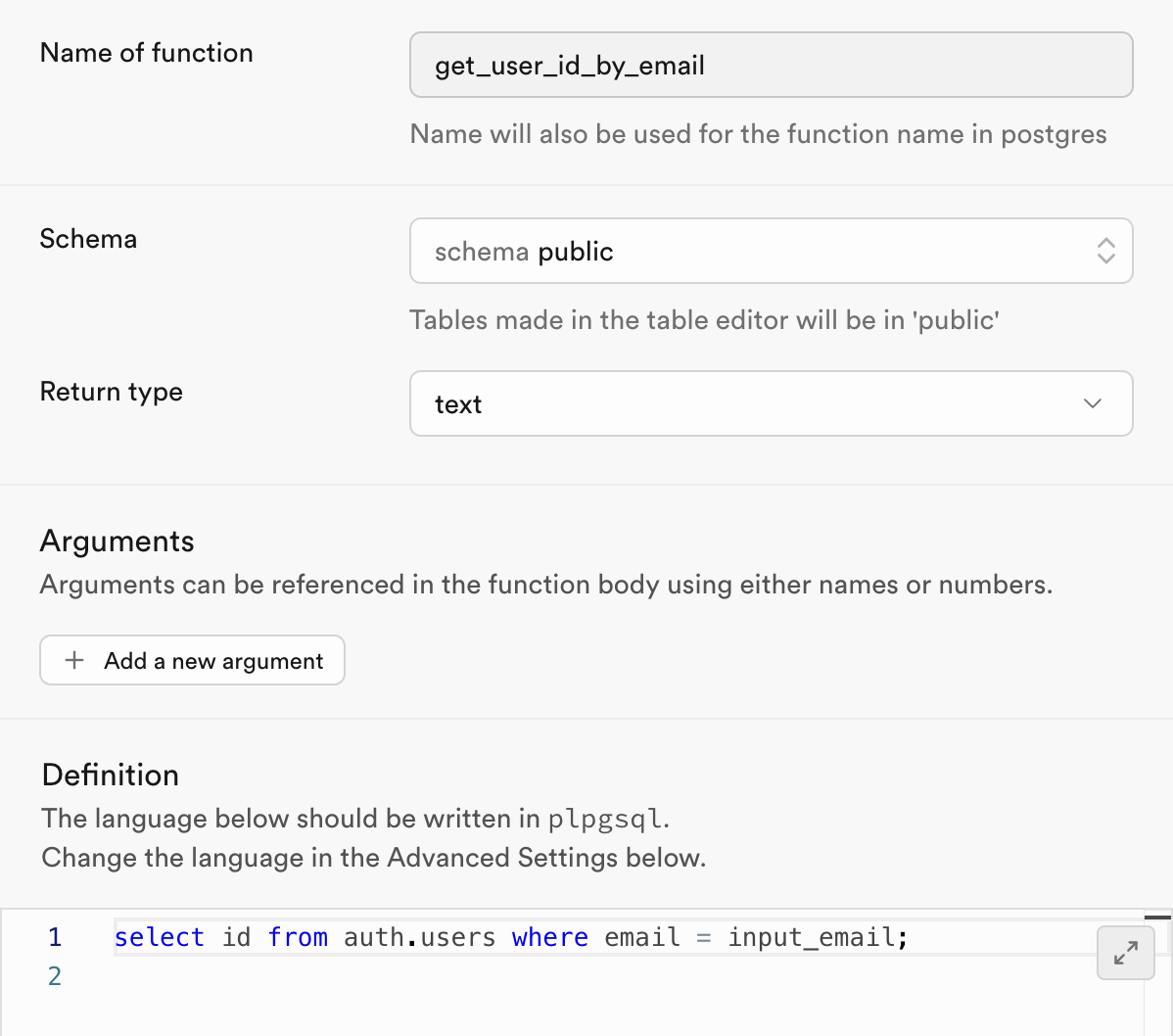
Step 4: Add an SQL Helper Function
For the supabase edge function, we'll also need an SQL function to get the id associated with a user with a given email
Navigate
to the Database Functions Page and
create new function called get_user_id_by_email with the following SQL:
select id from auth.users where email = input_email;
It should look like this:
Step 5: Create a Supabase Edge Function
Navigate to the Edge Functions Page and click Deploy New Function > Via Editor.
Enter the following code, give it the name polar-webhook and click on Deploy Function.
import "jsr:@supabase/functions-js/edge-runtime.d.ts"; import { createClient } from "jsr:@supabase/supabase-js@2"; import { validateEvent, WebhookVerificationError, } from "npm:@polar-sh/sdk@0.34.2/webhooks"; const secretKey = "POLAR_WEBHOOK_SECRET"; Deno.serve(async (req) => { const body = await req.text().catch( () => new Response("Invalid body", { status: 400, }), ); const supabaseClient = createClient( Deno.env.get("SUPABASE_URL"), Deno.env.get("SUPABASE_SERVICE_ROLE_KEY"), ); const secret = Deno.env.get(secretKey) ?? ""; try { const headers = Object.fromEntries(req.headers.entries()); const event = validateEvent(body, headers, secret); console.info({ event, }); switch (event.type) { case "subscription.created": case "subscription.updated": { event.data.customer.email; const { data: userId, error: userError } = await supabaseClient.rpc( "get_user_id_by_email", { input_email: event.data.customer.email, }, ); if (userError) { console.error("Error fetching user by email:", userError); return new Response("User fetch error", { status: 500, }); } const row = { user_id: userId, user_email: event.data.customer.email, modified_at: new Date(), subscription_id: event.data.id, subscription_status: event.data.status, subscription_starts_at: event.data.startedAt, subscription_ends_at: event.data.endsAt, subscription_price: event.data.amount, subscription_currency: event.data.currency, product_id: event.data.productId, product_name: event.data.product.name, product_recurring_interval: event.data.product.recurringInterval, raw_last_event: event, }; const { error } = await supabaseClient .from("subscriptions") .upsert(row, { onConflict: "user_id, subscription_id", }); if (error) { console.error("Error updating subscription", error); return new Response( "Error updating subscription: " + stringifyError(error), { status: 500, }, ); } return new Response("Handled event successfully.", { status: 200, }); } } return new Response("Ignored event successfully.", { status: 200, }); } catch (err) { console.error(err); if (err instanceof WebhookVerificationError) { return new Response("Forbidden", { status: 403, }); } return new Response("Error: " + stringifyError(err), { status: 400, }); } }); function stringifyError(error) { if (error instanceof Error) { return JSON.stringify( { name: error.name, message: error.message, stack: error.stack, }, null, 2, ); } return JSON.stringify(error); }
Copy the url of the edge function, you'll need it right away:
Step 6: Add A Webhook Endpoint to Polar
Now let's hop to the webhook settings page under Settings > Webhooks and click Add Endpoint.
Enter the url you copied from earlier, select the format Raw and select the events subscription.created and subsciption.updated.
Click on Create.
This will redirect you to the webhook details page where the secret is shown.
Copy this secret to a safe place (like a password manager) and let's hop back to Supabase.
Step 7: Set Up The Secret to Edge Function
The edge function needs the secret to make sure that no one can call your endpoint other than Polar.
Navigate to Edge Function Secrets and add a new Secret:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
POLAR_WEBHOOK_SECRET | <the copied secret> |
Step 8: Read the subscription state in the client
Last but not least, you can now read the subscription state on the client!
Here's an example in TypeScript:
async function isPro() { const { data: subscriptions, error } = await supabase .from("subscriptions") .select("*") .eq("user_id", data.id); if (error) throw new Error(error.message); return subscriptions.some((sub) => dayjs().isBetween(sub.subscription_starts_at, sub.subscription_ends_at), ); }
Wrapping Up
Woohoo! 🎉
You've successfully integrated Polar with Supabase using Edge Functions!